Sensor: Aura > OMI
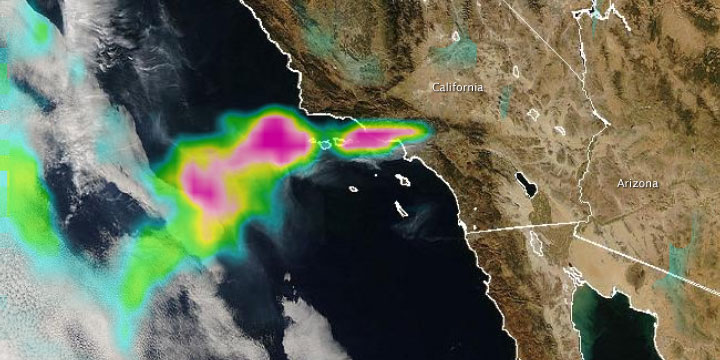
Fires in California
Published November 18, 2008
Smoke from the recent outbreak of fires in Southern California can clearly be seen from NASA satellites.
Related images:
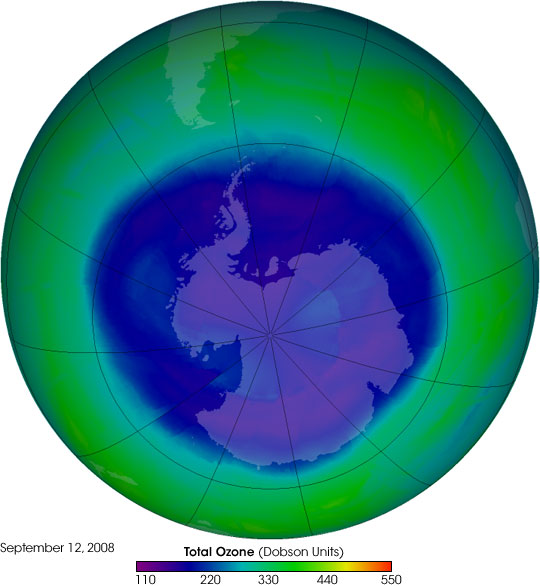
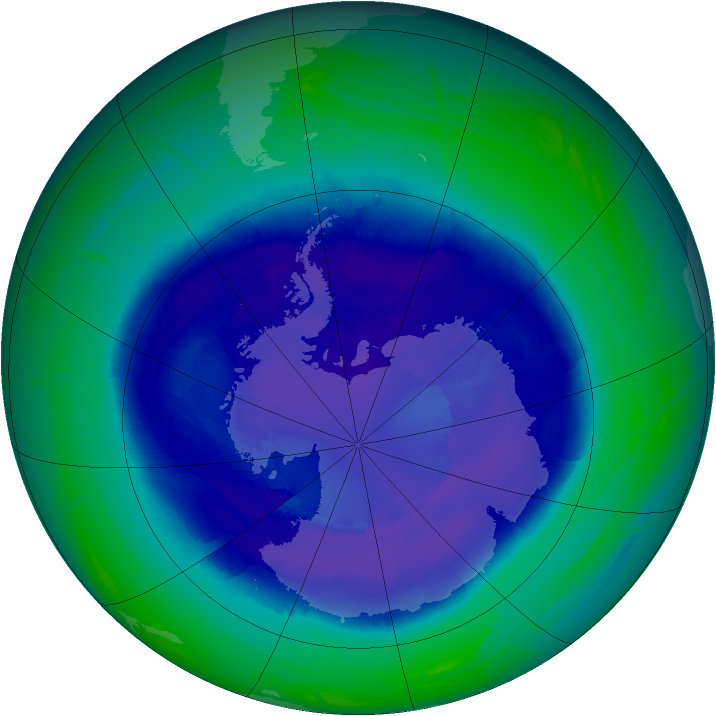
The Ozone Hole of 2008
Published October 25, 2008
On September 12, 2008, the Antarctic ozone hole reached its maximum size for the year.
Related images:
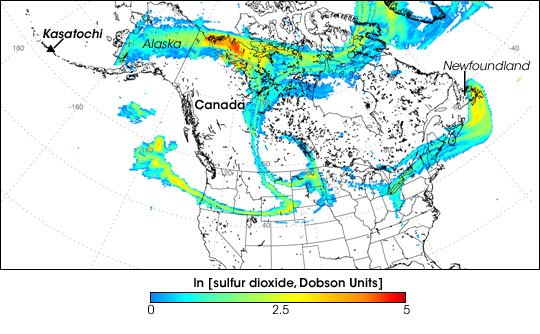
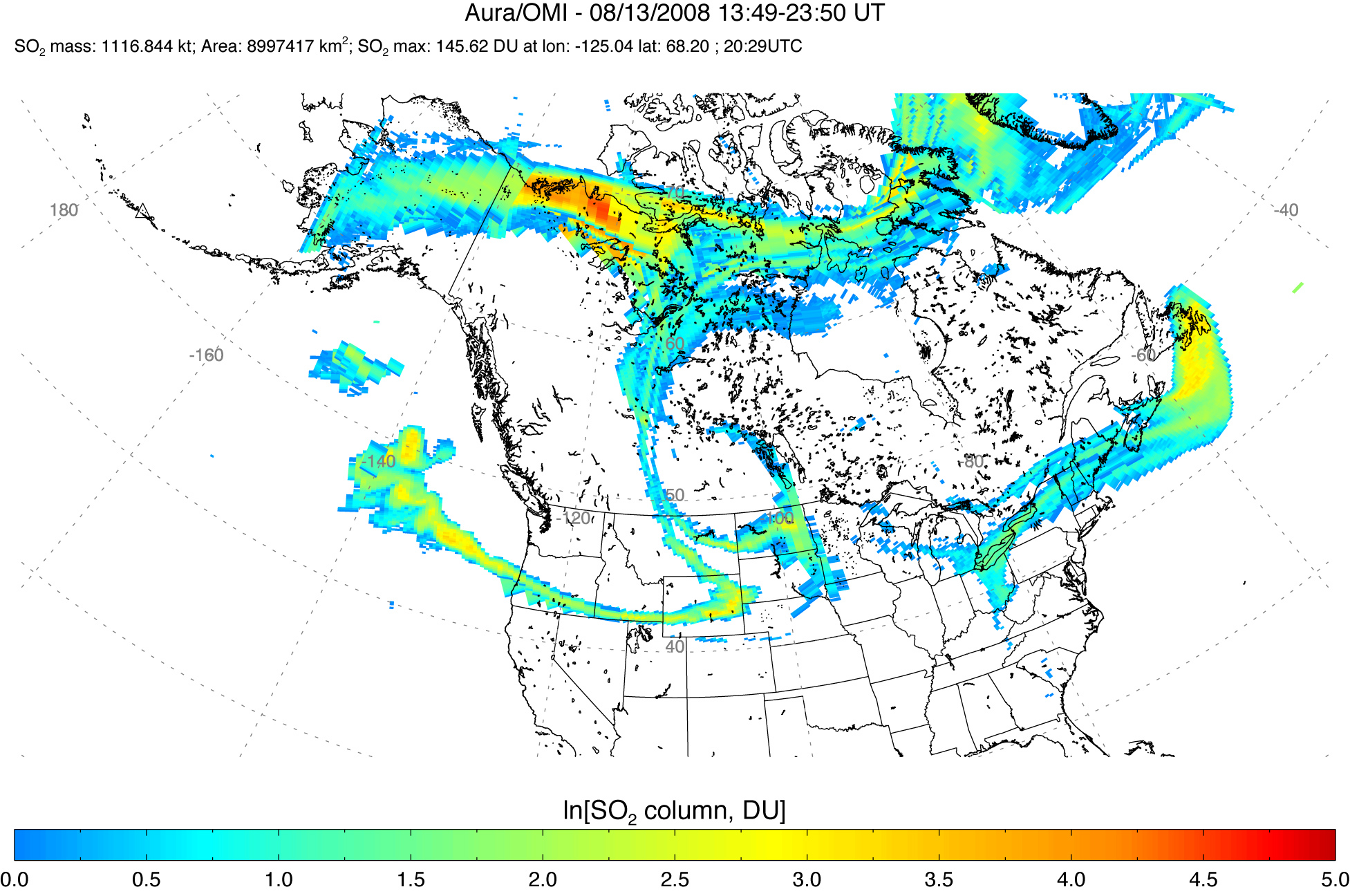
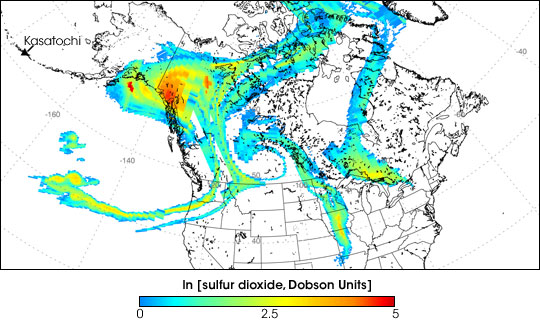
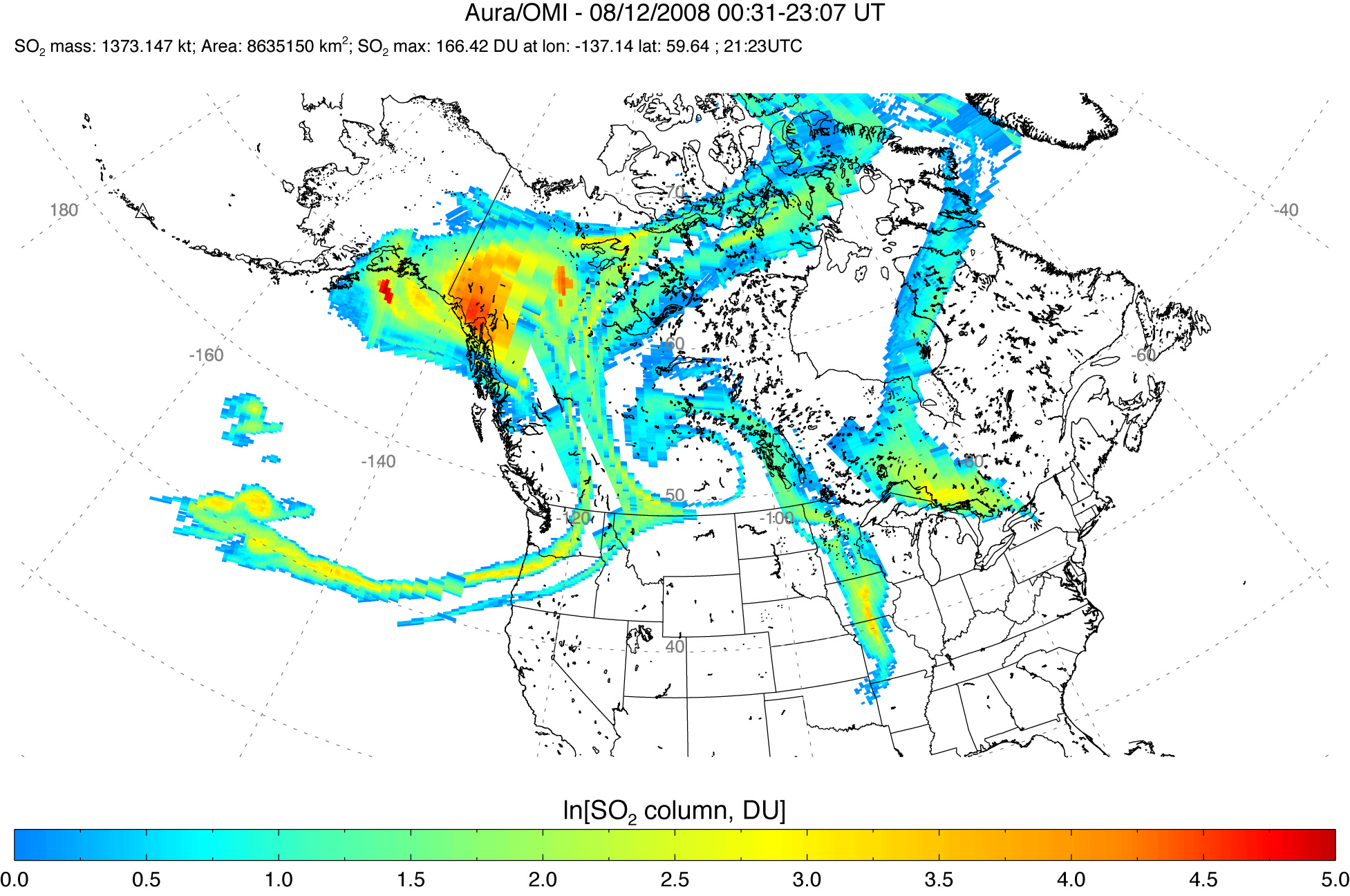
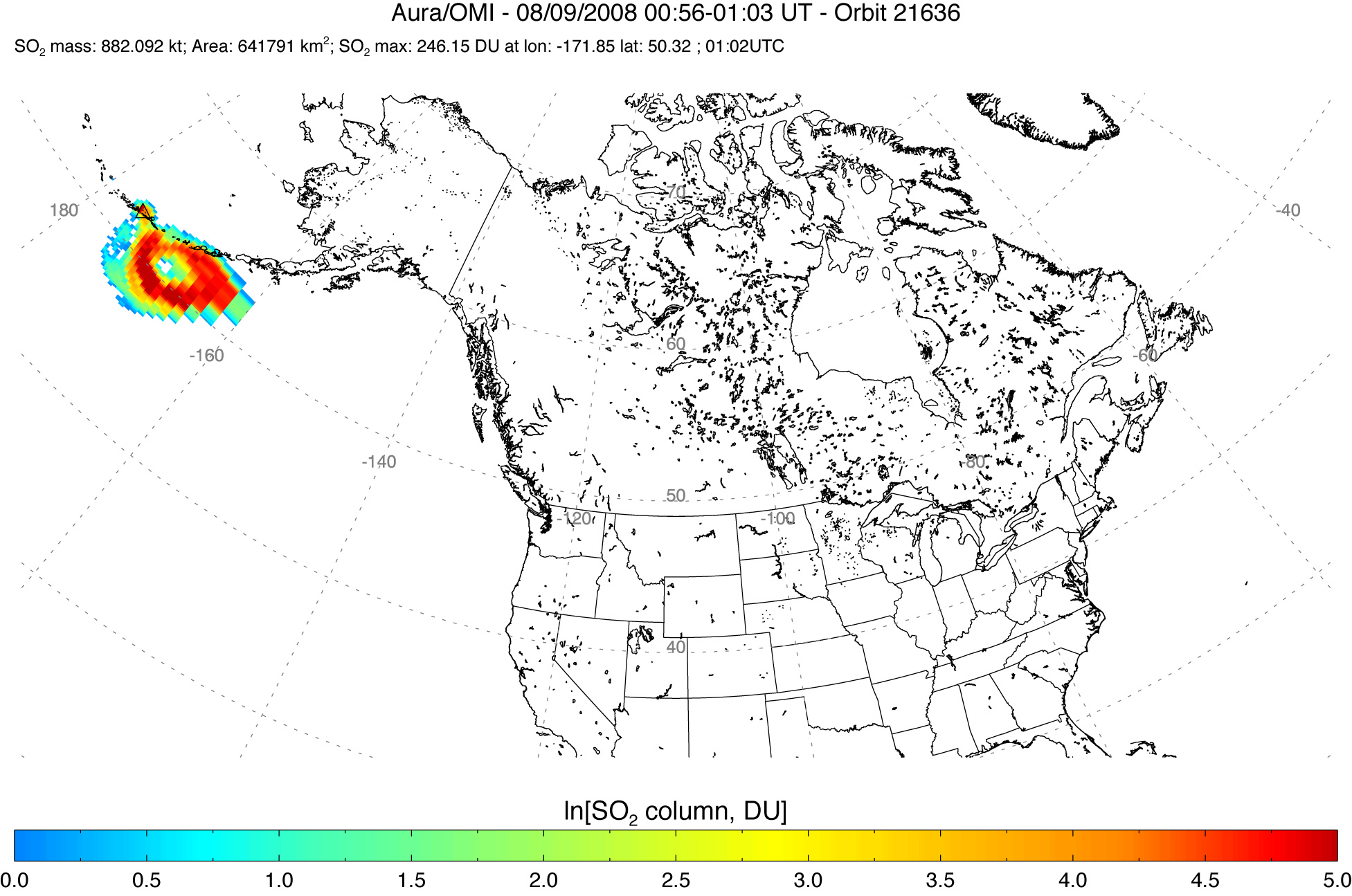
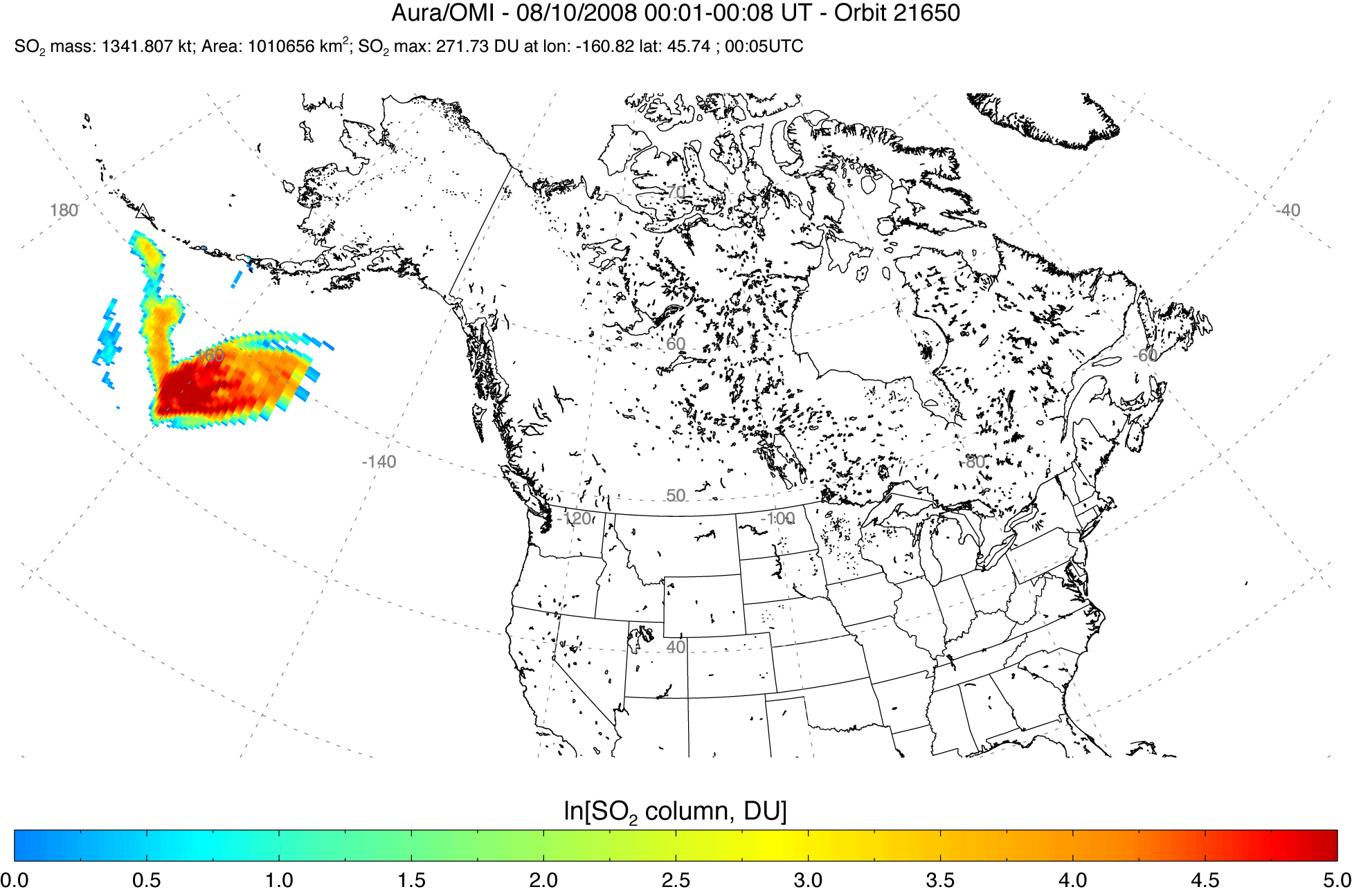
Sulfur Dioxide Cloud from Aleutians’ Kasatochi Volcano
Published August 13, 2008
Between August 7 and August 8, 2008, three explosive eruptions rocked the Kasatochi Volcano in the Aleutian Islands of Alaska. In addition to sending a thick plume of ash at least 35,000 feet into the atmosphere, the volcano released a large cloud of sulfur dioxide.
Related images:
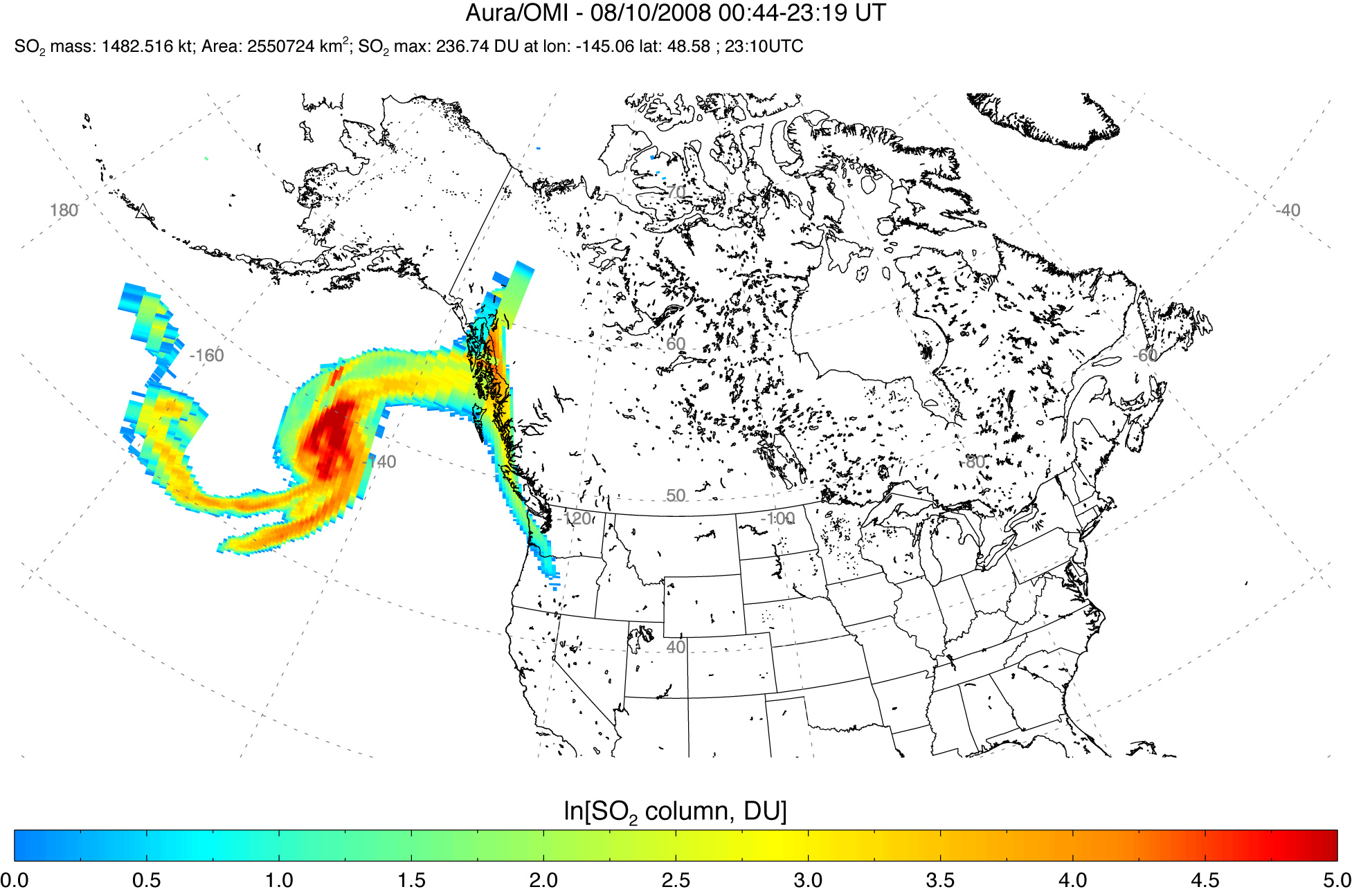
Sulfur Dioxide Cloud from Aleutians’ Kasatochi Volcano
Published August 13, 2008
Between August 7 and August 8, 2008, three explosive eruptions rocked the Kasatochi Volcano in the Aleutian Islands of Alaska. In addition to sending a thick plume of ash at least 35,000 feet into the atmosphere, the volcano released a large cloud of sulfur dioxide.
Related images:
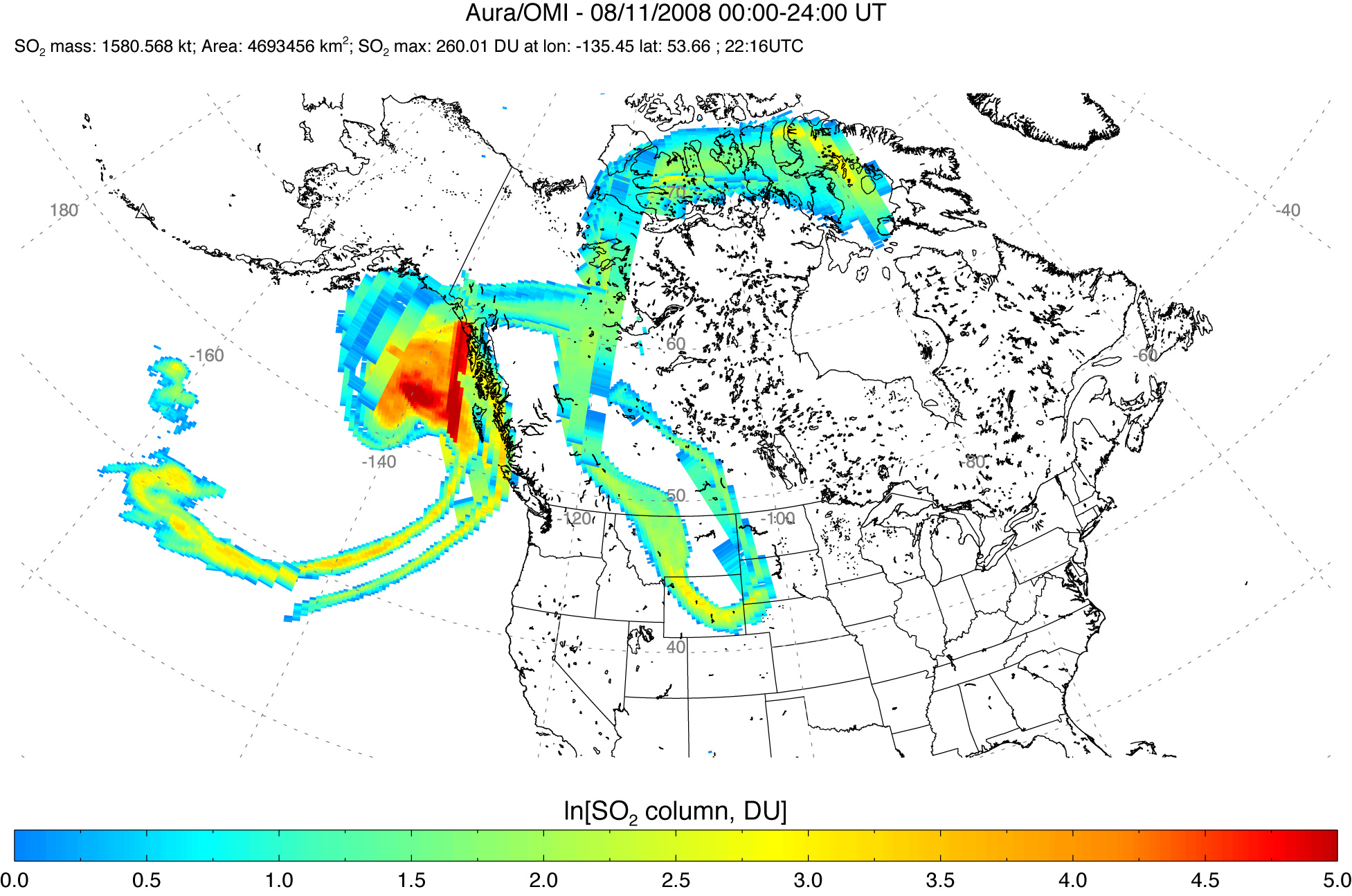
Sulfur Dioxide Cloud from Aleutians’ Kasatochi Volcano
Published August 13, 2008
Between August 7 and August 8, 2008, three explosive eruptions rocked the Kasatochi Volcano in the Aleutian Islands of Alaska. In addition to sending a thick plume of ash at least 35,000 feet into the atmosphere, the volcano released a large cloud of sulfur dioxide.
Related images:
Sulfur Dioxide Cloud from Aleutians’ Kasatochi Volcano
Published August 13, 2008
Between August 7 and August 8, 2008, three explosive eruptions rocked the Kasatochi Volcano in the Aleutian Islands of Alaska. In addition to sending a thick plume of ash at least 35,000 feet into the atmosphere, the volcano released a large cloud of sulfur dioxide.
Related images:
Sulfur Dioxide Cloud from Aleutians’ Kasatochi Volcano
Published August 13, 2008
Between August 7 and August 8, 2008, three explosive eruptions rocked the Kasatochi Volcano in the Aleutian Islands of Alaska. In addition to sending a thick plume of ash at least 35,000 feet into the atmosphere, the volcano released a large cloud of sulfur dioxide.
Related images:
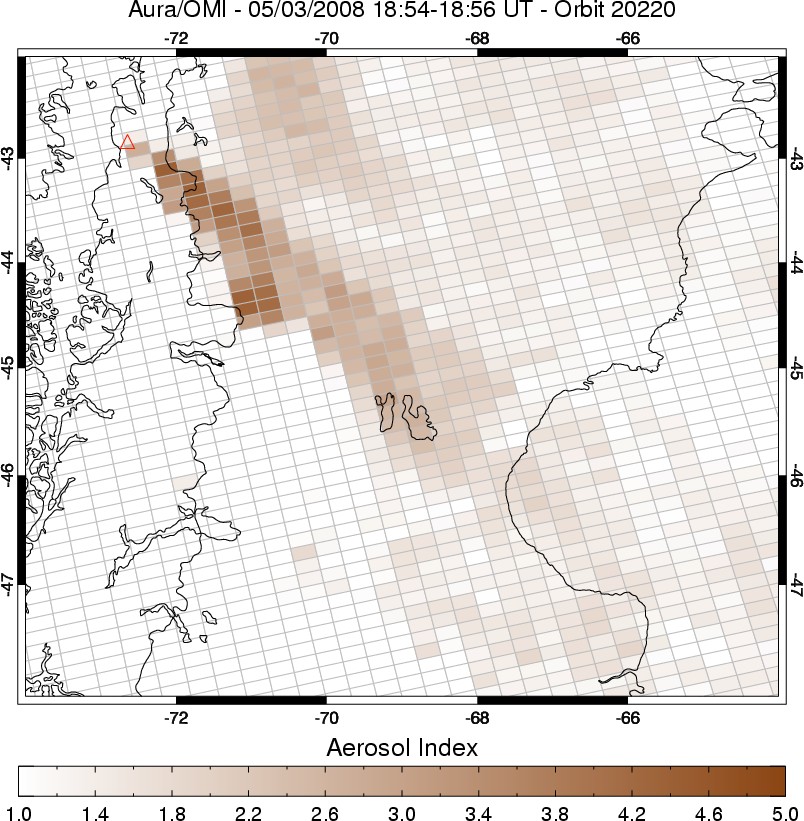
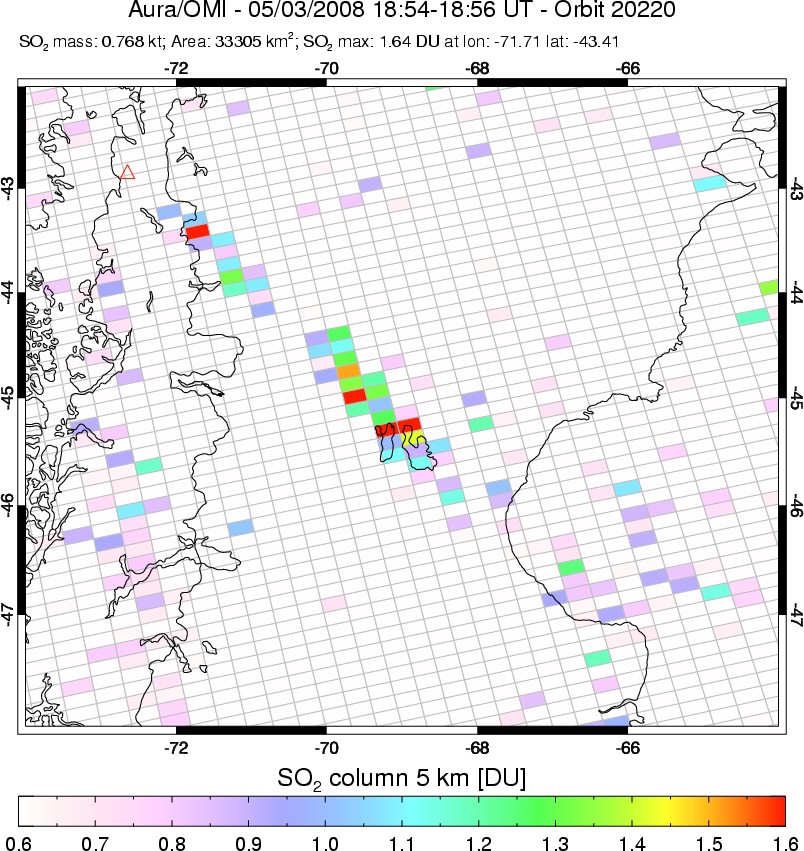
Aerosols from Chaiten Volcano
Published May 24, 2008
On May 2, 2008, the Chaiten Volcano of southern Chile rumbled to life, also sending a cloud of ash high into the atmosphere.
Related images:
Aerosols from Chaiten Volcano
Published May 24, 2008
On May 2, 2008, the Chaiten Volcano of southern Chile rumbled to life, also sending a cloud of ash high into the atmosphere.
Related images:
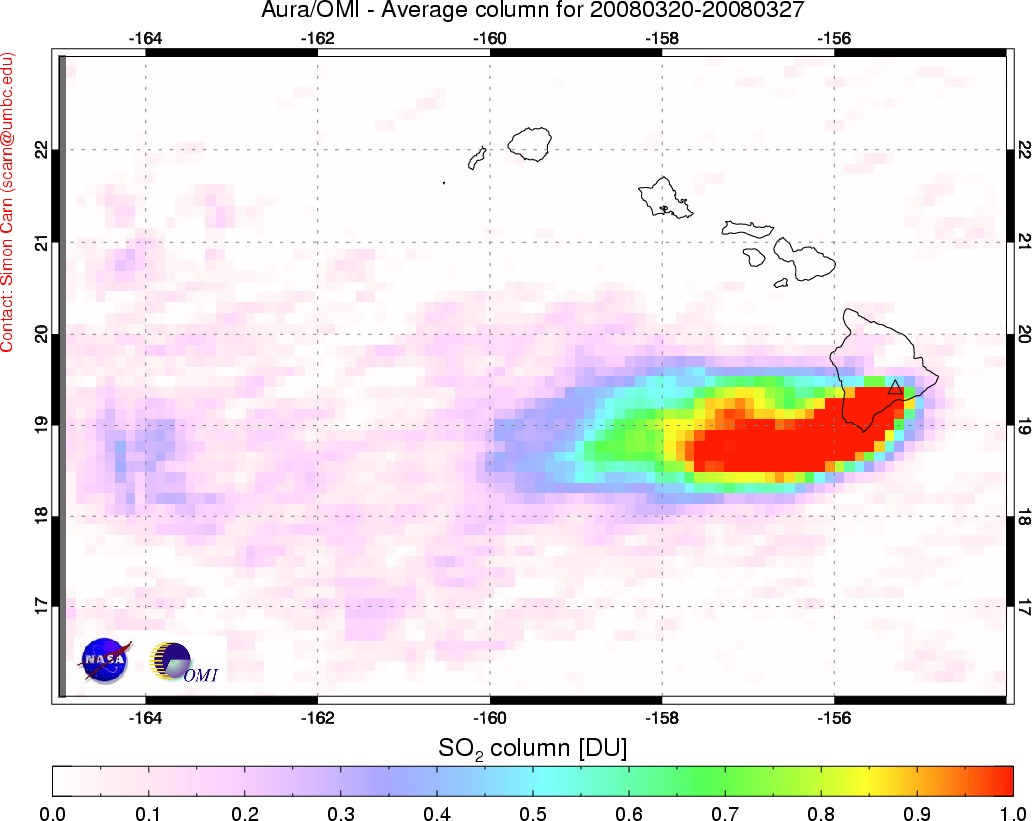
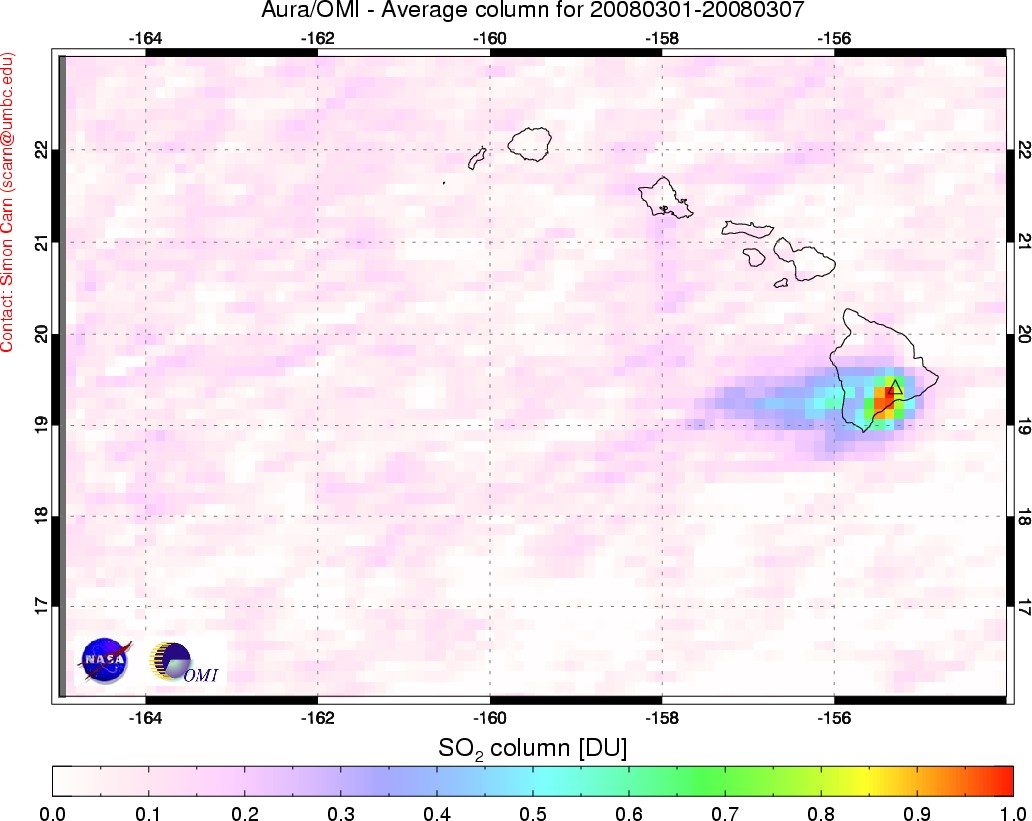
Sulfur Dioxide Plume from Kilauea
Published March 29, 2008
Kilauea is one of the world’s most active volcanoes, but it is of the sort that tends to ooze lava more often than it explodes. But starting on March 19, a small explosion rained rock and ash over the summit. The Hawaiian Volcano Observatory warned on March 28 that sulfur dioxide concentrations in the air downwind from the volcano were likely to be hazardous. Even before the March 19 explosion, elevated sulfur dioxide levels prompted the National Park Service to close part of Crater Rim Drive.
Related images: