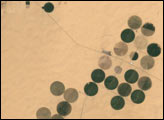
Irrigation in the Heart of the Sahara
Published March 2, 2002
Although it is now the largest desert on Earth, during the last ice age the Sahara was a savannah with a climate similar to that of present-day Kenya and Tanzania. The annual rainfall was much greater than it is now, creating many rivers and lakes that are now hidden under shifting sands or exposed as barren salt flats. Over several hundred thousand years, the rains also filled a series of vast underground aquifers. Modern African nations are now mining this fossil water to support irrigated farming projects.
Related images:
Irrigation in the Heart of the Sahara
Published March 2, 2002
Although it is now the largest desert on Earth, during the last ice age the Sahara was a savannah with a climate similar to that of present-day Kenya and Tanzania. The annual rainfall was much greater than it is now, creating many rivers and lakes that are now hidden under shifting sands or exposed as barren salt flats. Over several hundred thousand years, the rains also filled a series of vast underground aquifers. Modern African nations are now mining this fossil water to support irrigated farming projects.
Related images:
Irrigation in the Heart of the Sahara
Published March 2, 2002
Although it is now the largest desert on Earth, during the last ice age the Sahara was a savannah with a climate similar to that of present-day Kenya and Tanzania. The annual rainfall was much greater than it is now, creating many rivers and lakes that are now hidden under shifting sands or exposed as barren salt flats. Over several hundred thousand years, the rains also filled a series of vast underground aquifers. Modern African nations are now mining this fossil water to support irrigated farming projects.
Related images:
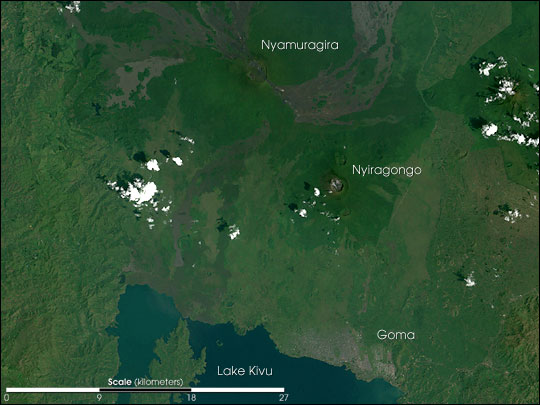
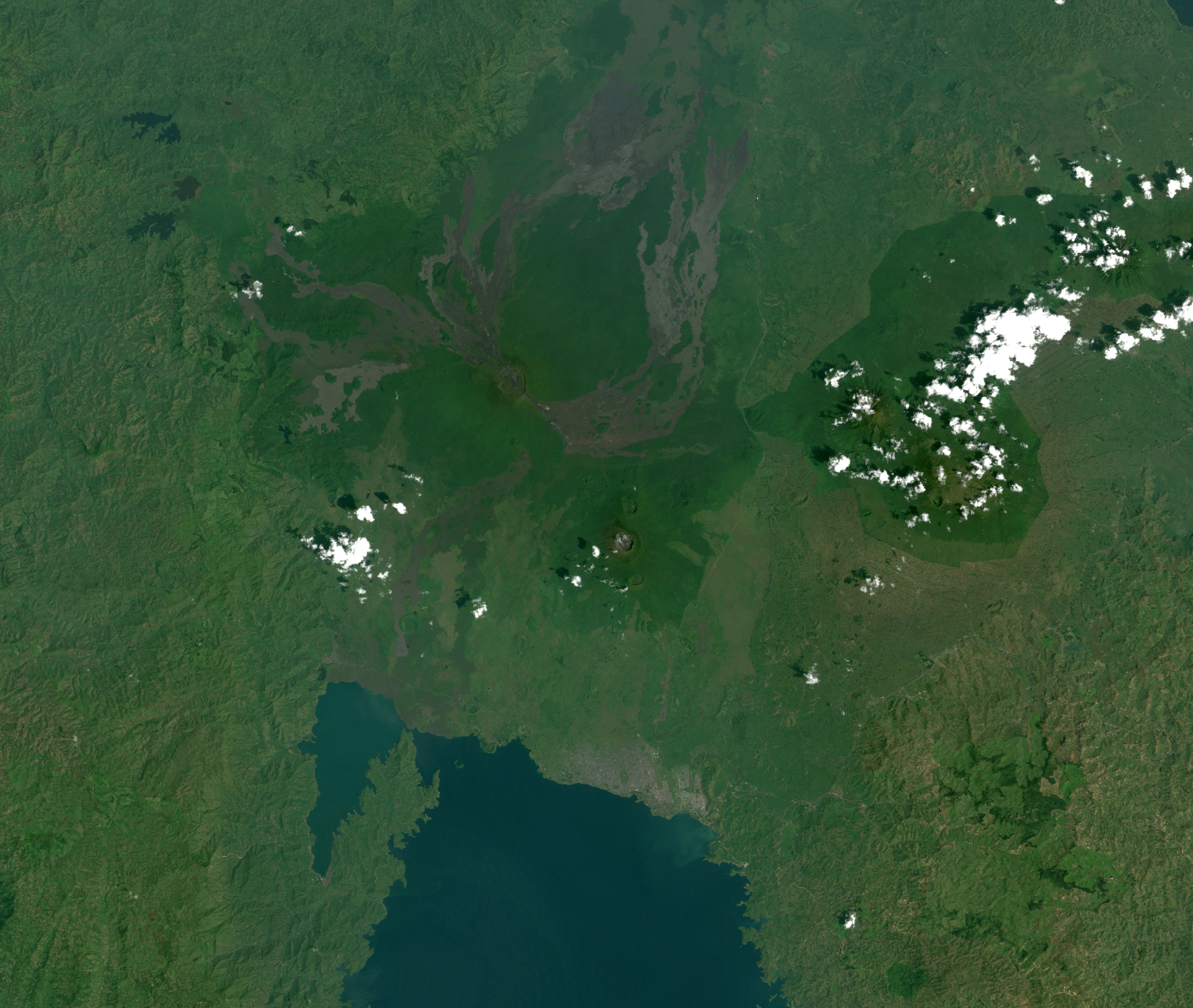
Akpatok Island
Published February 25, 2002
Akpatok Island lies in Ungava Bay in northern Quebec, Canada. Accessible only by air, Akpatok Island rises out of the water as sheer cliffs that soar 500 to 800 feet (150 to 243 m) above the sea surface. The island is an important sanctuary for cliff-nesting seabirds.
Related images:
Akpatok Island
Published February 25, 2002
Akpatok Island lies in Ungava Bay in northern Quebec, Canada. Accessible only by air, Akpatok Island rises out of the water as sheer cliffs that soar 500 to 800 feet (150 to 243 m) above the sea surface. The island is an important sanctuary for cliff-nesting seabirds.
Related images:
Akpatok Island
Published February 25, 2002
Akpatok Island lies in Ungava Bay in northern Quebec, Canada. Accessible only by air, Akpatok Island rises out of the water as sheer cliffs that soar 500 to 800 feet (150 to 243 m) above the sea surface. The island is an important sanctuary for cliff-nesting seabirds.
Related images:
Akpatok Island
Published February 25, 2002
Akpatok Island lies in Ungava Bay in northern Quebec, Canada. Accessible only by air, Akpatok Island rises out of the water as sheer cliffs that soar 500 to 800 feet (150 to 243 m) above the sea surface. The island is an important sanctuary for cliff-nesting seabirds.
Related images:
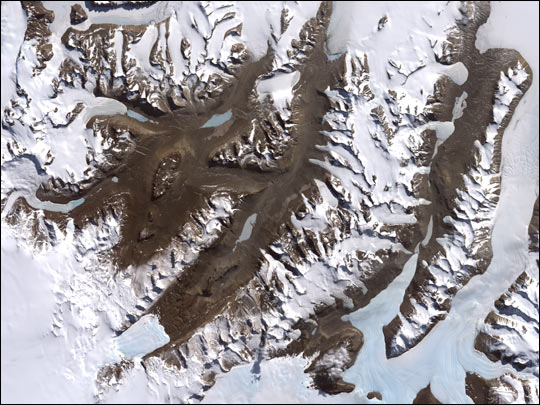
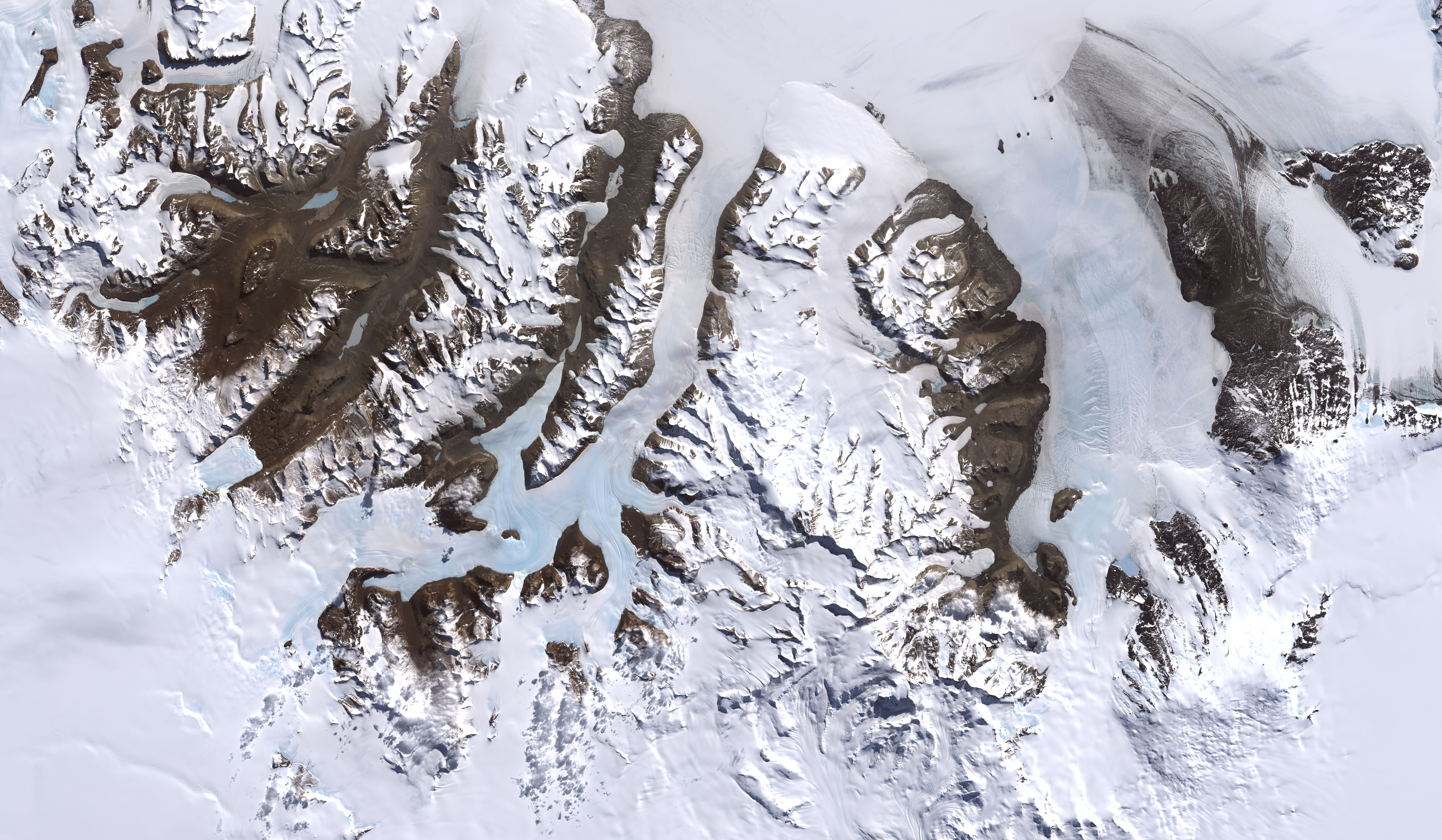
McMurdo Dry Valleys
Published January 26, 2002
One of the few areas of Antarctica not covered by thousands of meters of ice, the McMurdo Dry Valleys stand out in this satellite image. For a few weeks each summer temperatures are warm enough to melt glacial ice, creating streams that feed freshwater lakes that lie at the bottom of the valleys.
Related images:
McMurdo Dry Valleys
Published January 26, 2002
One of the few areas of Antarctica not covered by thousands of meters of ice, the McMurdo Dry Valleys stand out in this satellite image. For a few weeks each summer temperatures are warm enough to melt glacial ice, creating streams that feed freshwater lakes that lie at the bottom of the valleys.
Related images:
McMurdo Dry Valleys
Published January 26, 2002
One of the few areas of Antarctica not covered by thousands of meters of ice, the McMurdo Dry Valleys stand out in this satellite image. For a few weeks each summer temperatures are warm enough to melt glacial ice, creating streams that feed freshwater lakes that lie at the bottom of the valleys.
Related images: