NASA satellites and sensors constantly take the pulse of our planet, measuring how Earth changes by the day, season, year, and decade. Researchers and resource managers analyze those measurements and apply them on local and regional scales to better manage things like our food and water supplies, health, safety, land use, and ecosystems. NASA data is also used by other government agencies to help with responses to natural disasters and emergencies around the country and the world.
Western Mountain Snow Melts Fast and Early
Published June 28, 2025
A warm and dry spring in the Pacific Northwest quickly depleted the seasonal snowpack, raising concern over summer water supplies and wildland fire risk.
Related images:
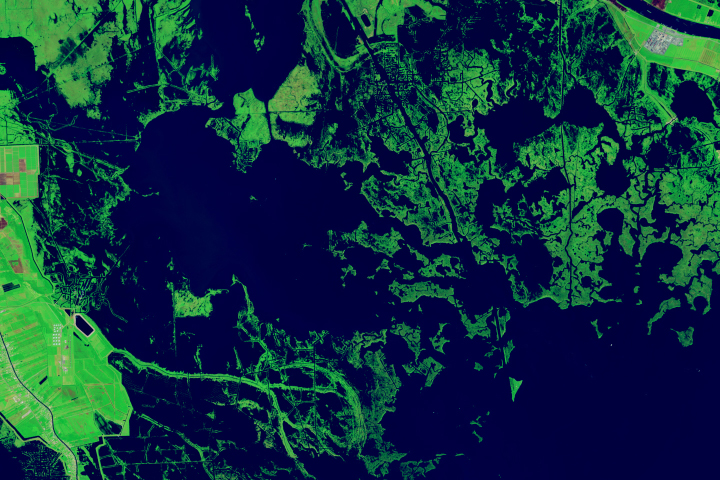
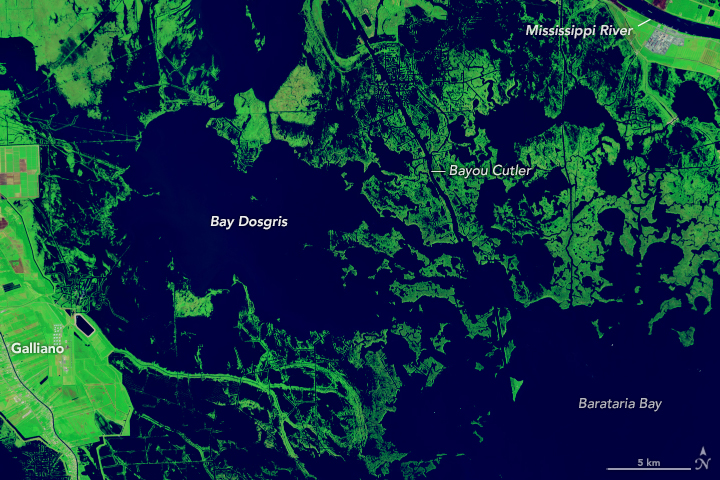
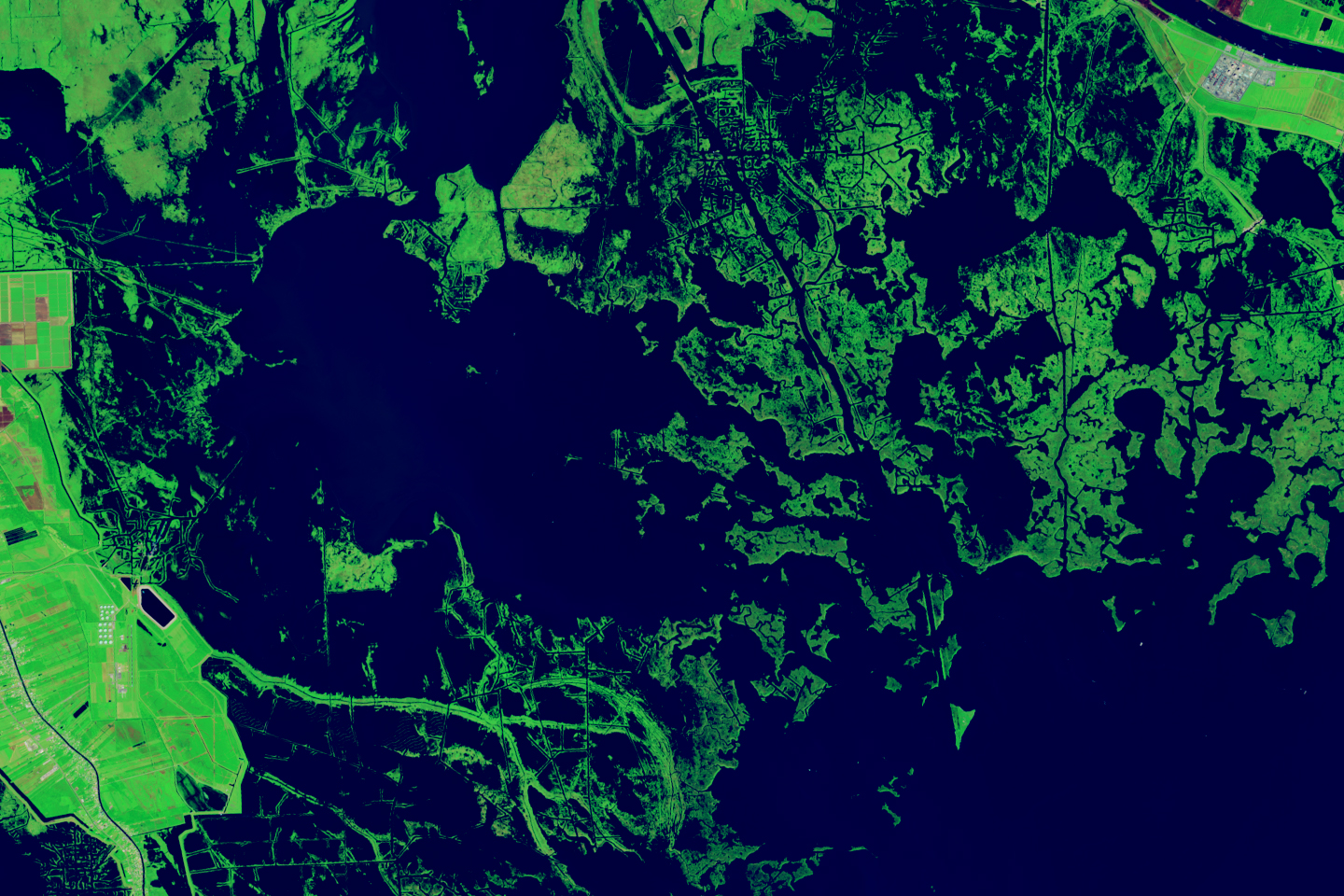
Forty Years of Change in Louisiana’s Wetlands
Published May 19, 2025
Scientists used Landsat satellite images to detect both abrupt and gradual changes and to examine how phenomena, from storms to sea level rise, have reshaped coastal ecosystems.
Related images:
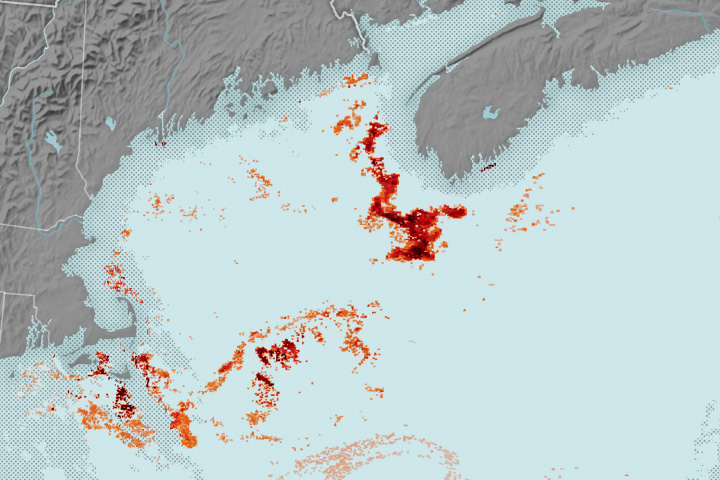
Mapping the Tiny Plankton That Feed Giant Right Whales
Published May 12, 2025
Researchers used NASA satellite data to detect swarms of red-tinged copepods, a key food source for the endangered marine mammals, in the Gulf of Maine.
Related images:
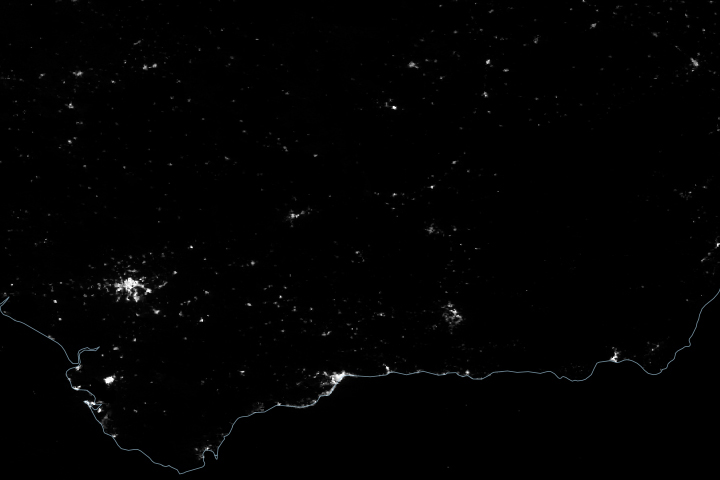
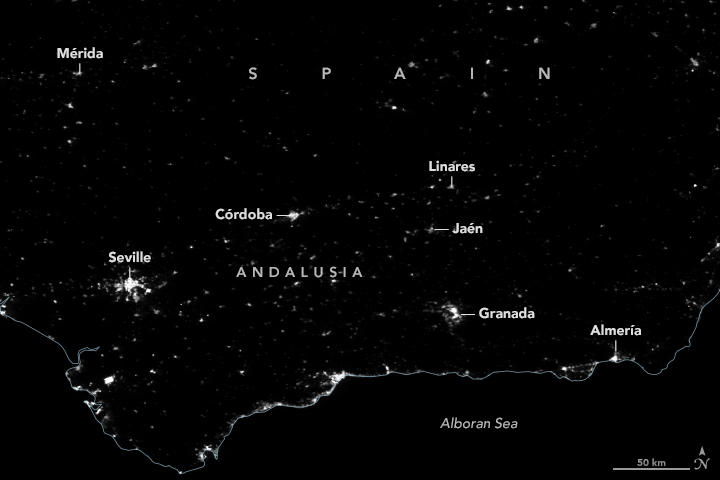
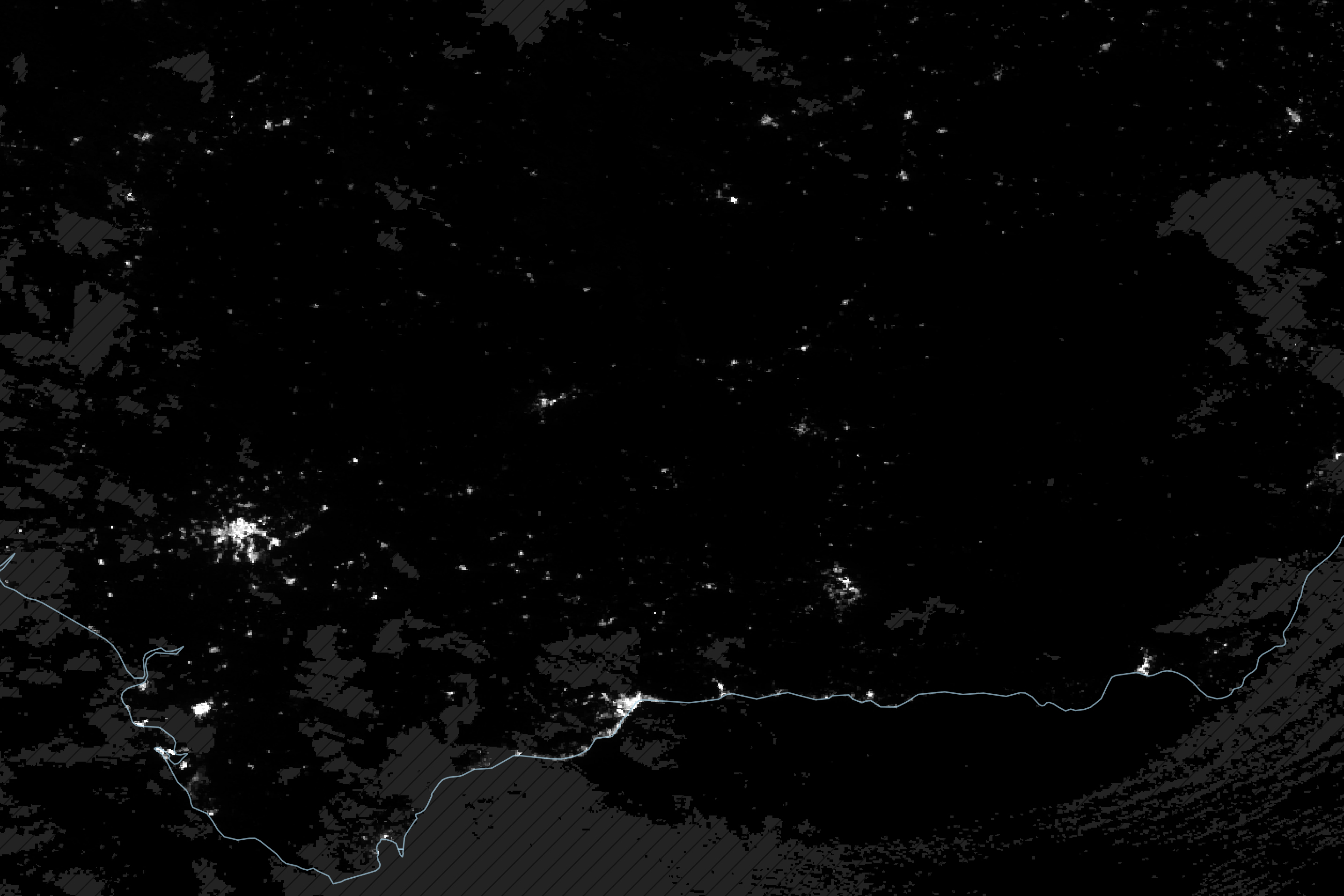
Blackout in Andalusia
Published May 1, 2025
Satellite-derived maps of nighttime lights in southern Spain revealed power outages that persisted across rural areas as the region was recovering from a widespread blackout.
Related images:
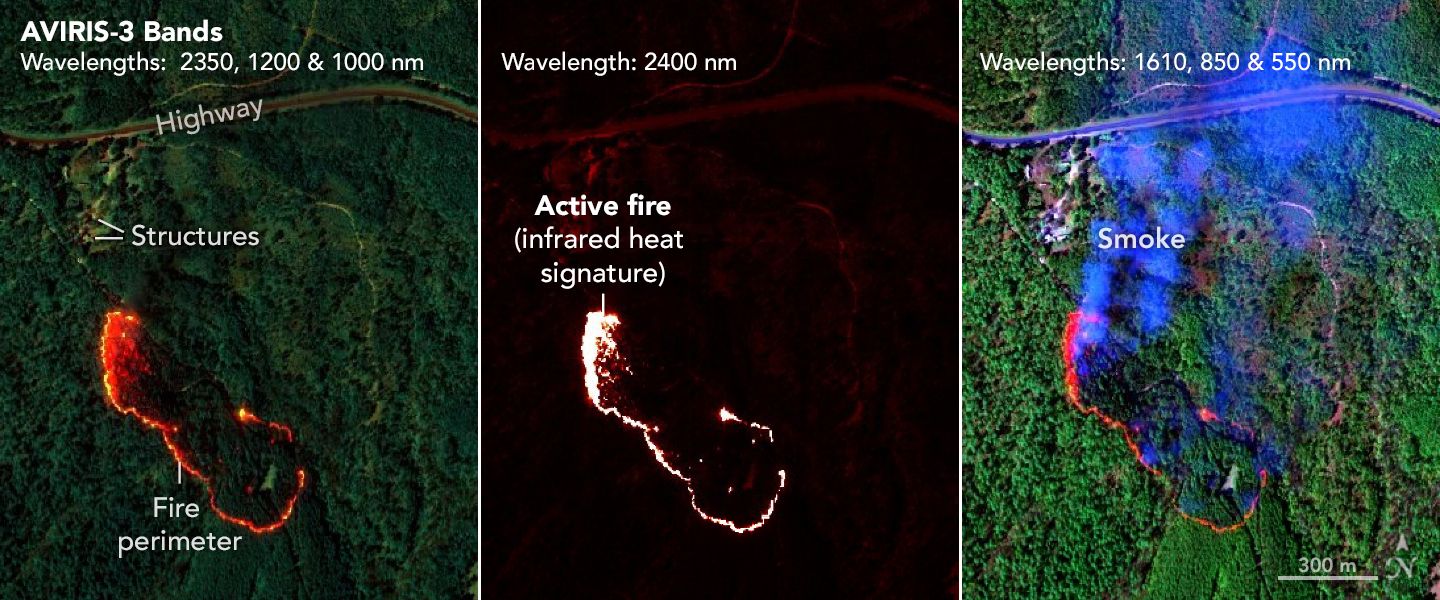
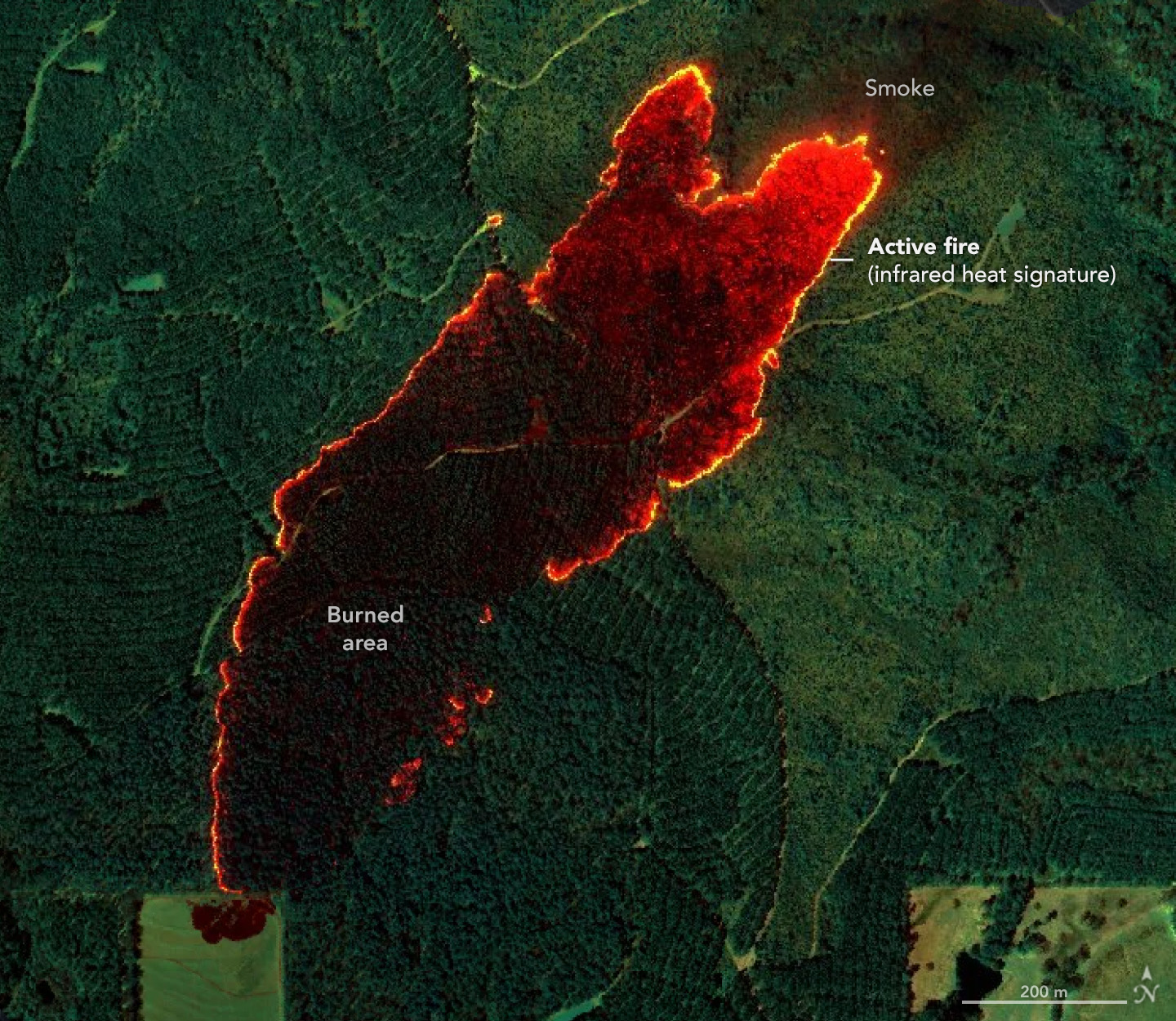
Wildfire Maps Help Firefighters in Real Time
Published April 29, 2025
Detailed fire maps, produced in minutes with data from a NASA airborne sensor, enabled firefighters in Alabama to limit the spread of wildfires and save buildings.
Related images:
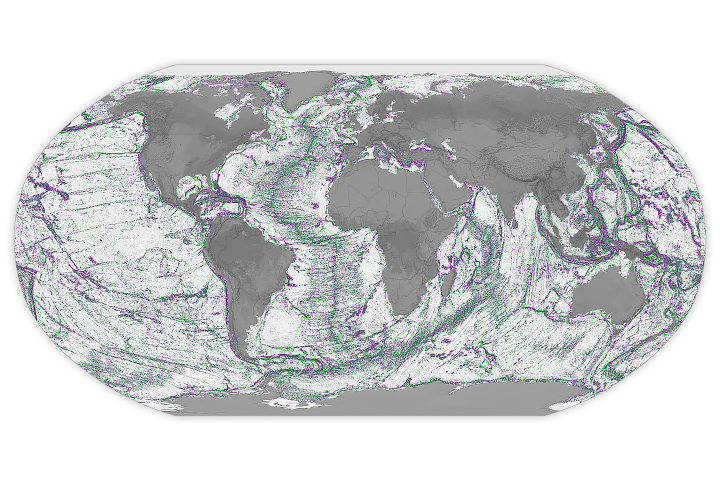
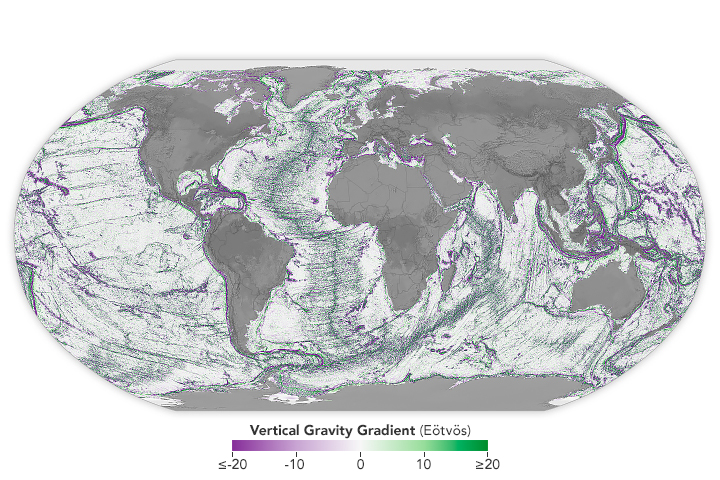
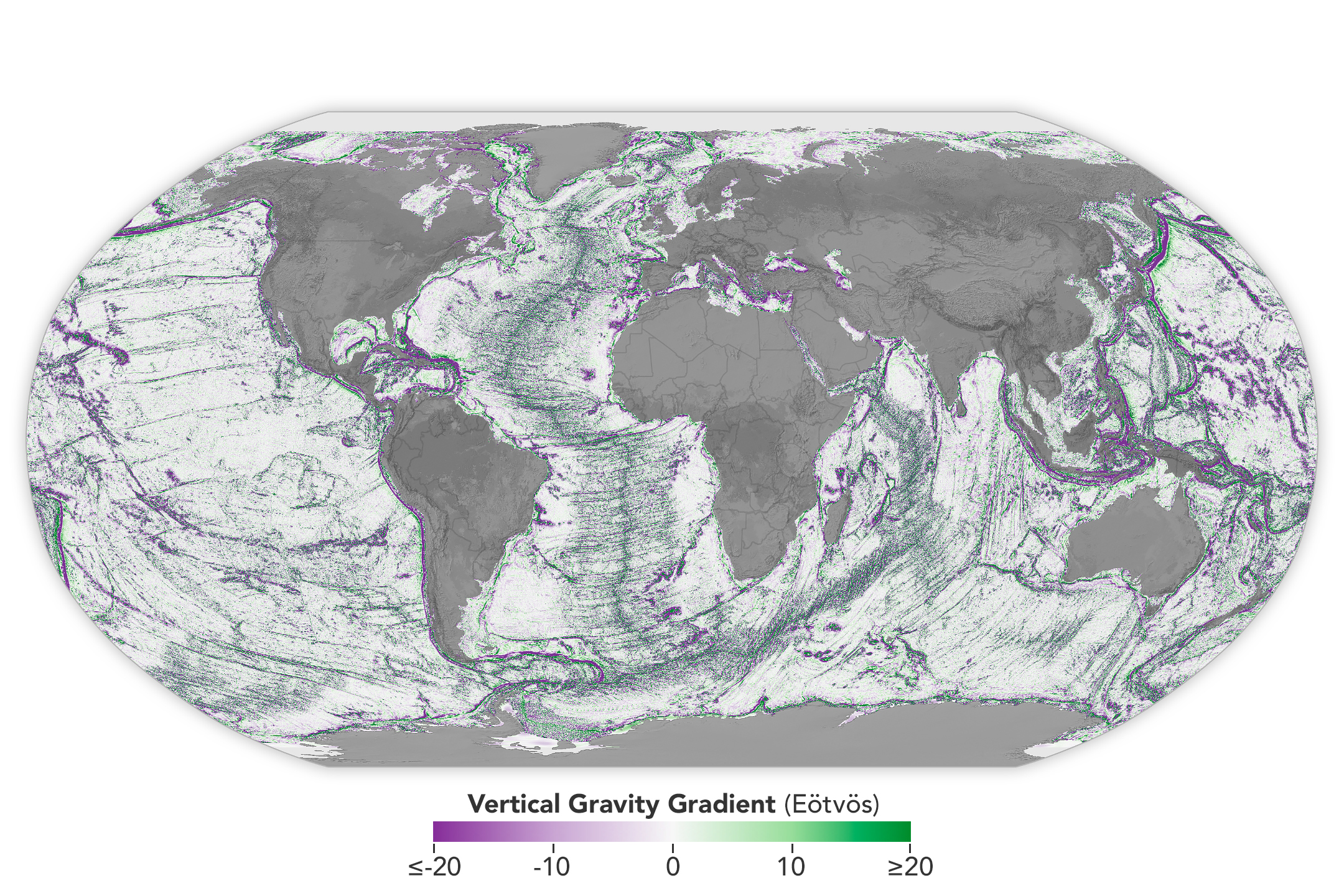
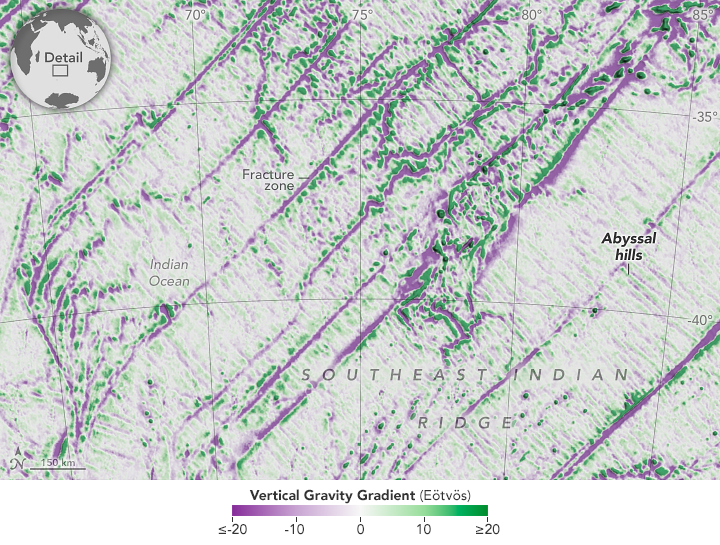
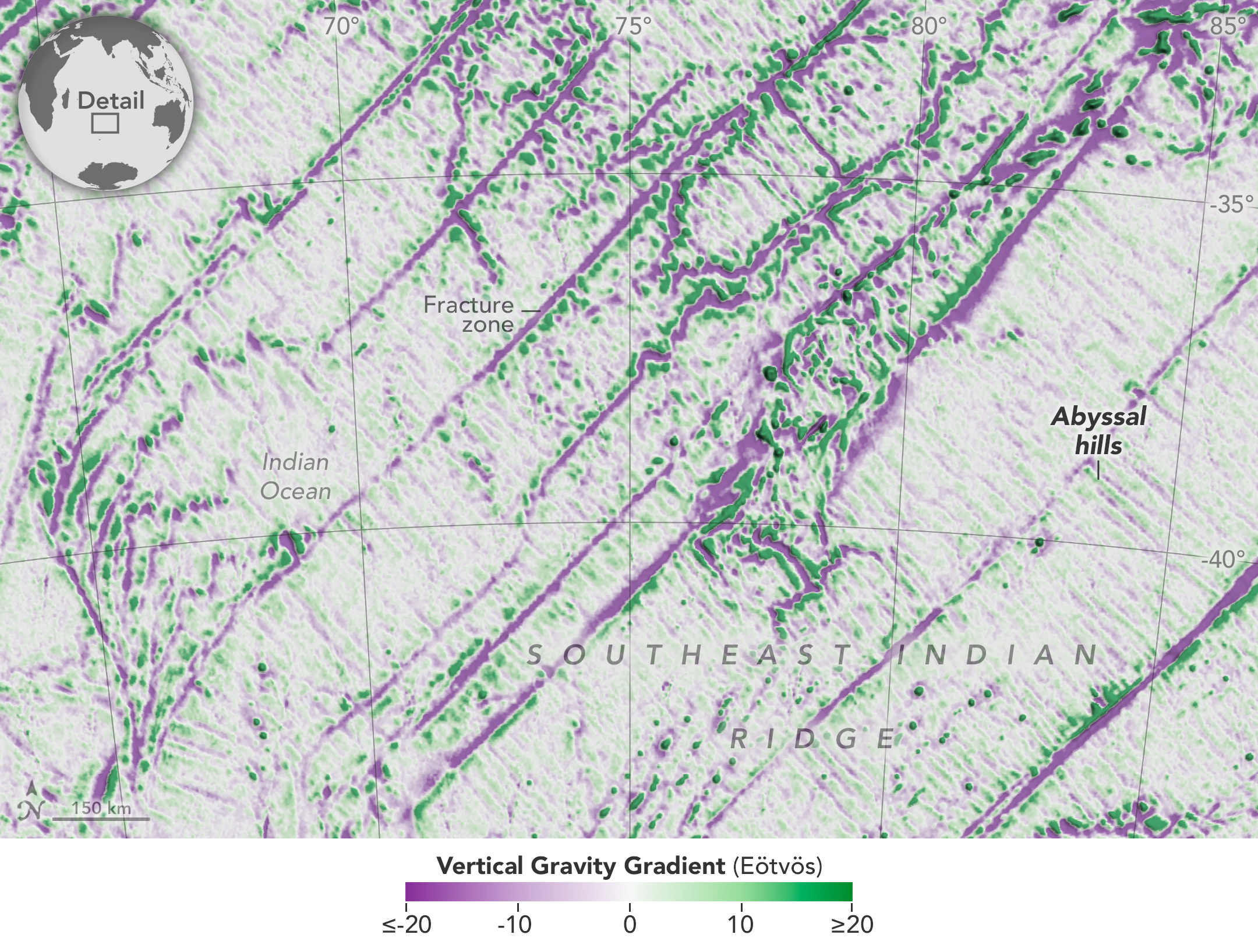
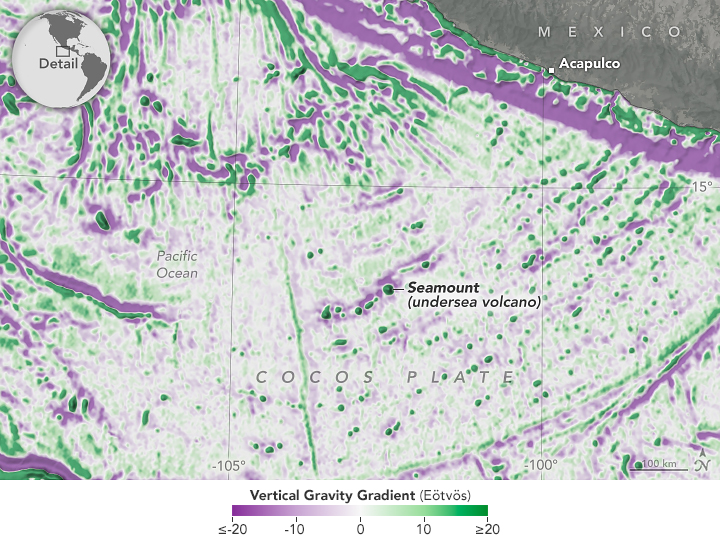
Seamounts and Abyssal Hills Mapped From Space
Published April 1, 2025
Depictions of the seafloor derived from satellite data can improve underwater navigation and increase knowledge of how heat and life move around the world’s ocean.
Related images:
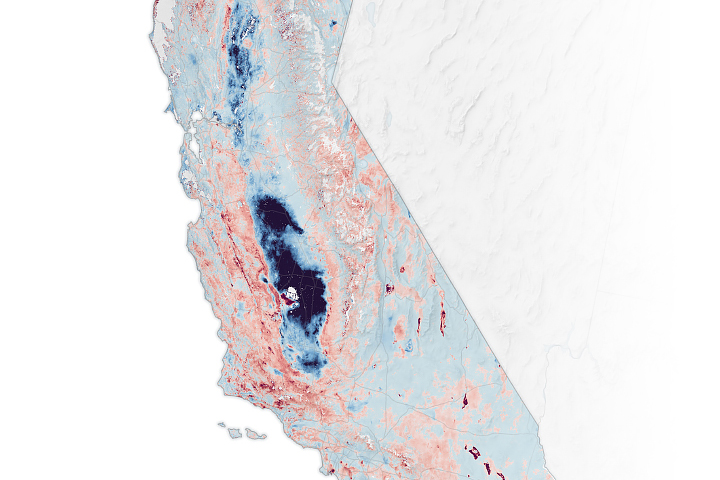
Where California’s Land Is Sinking and Rising
Published February 22, 2025
The elevation changes may seem small, amounting to fractions of inches per year, but they can increase or decrease local flood risk, wave exposure, and saltwater intrusion.
Related images:
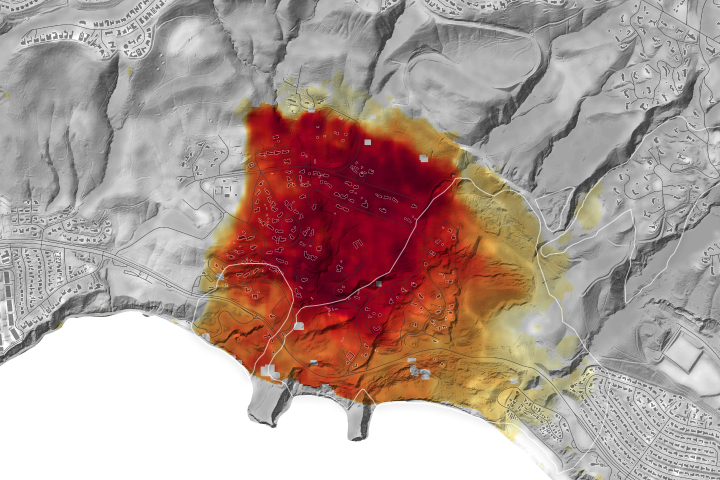
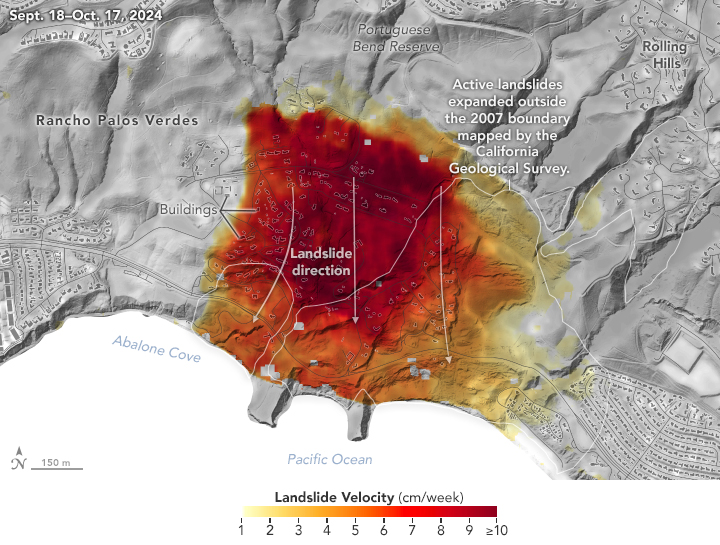
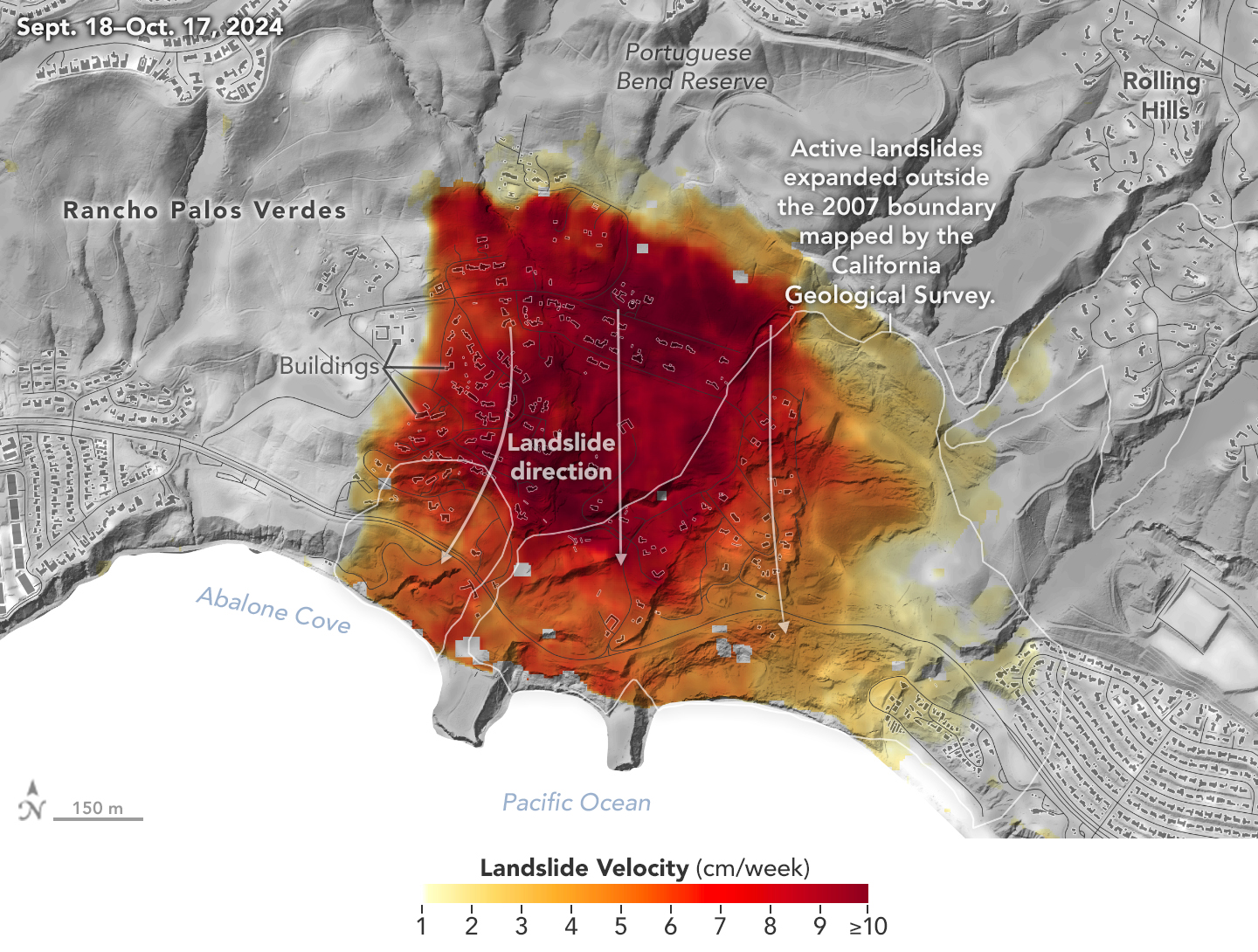
Los Angeles-Area Landslide Expands
Published February 6, 2025
NASA radar imagery revealed that the active area of a decades-old landslide has grown following periods of heavy rainfall in 2023 and early 2024.
Related images:
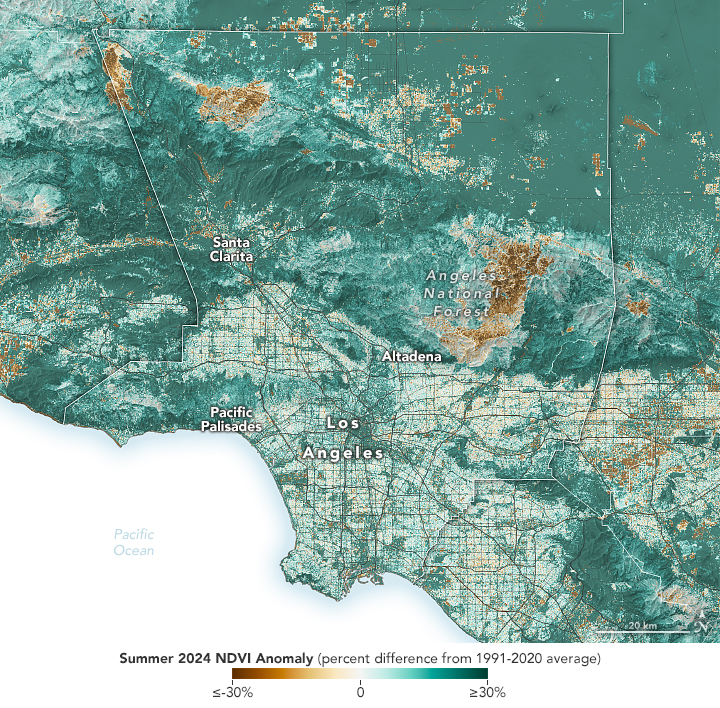
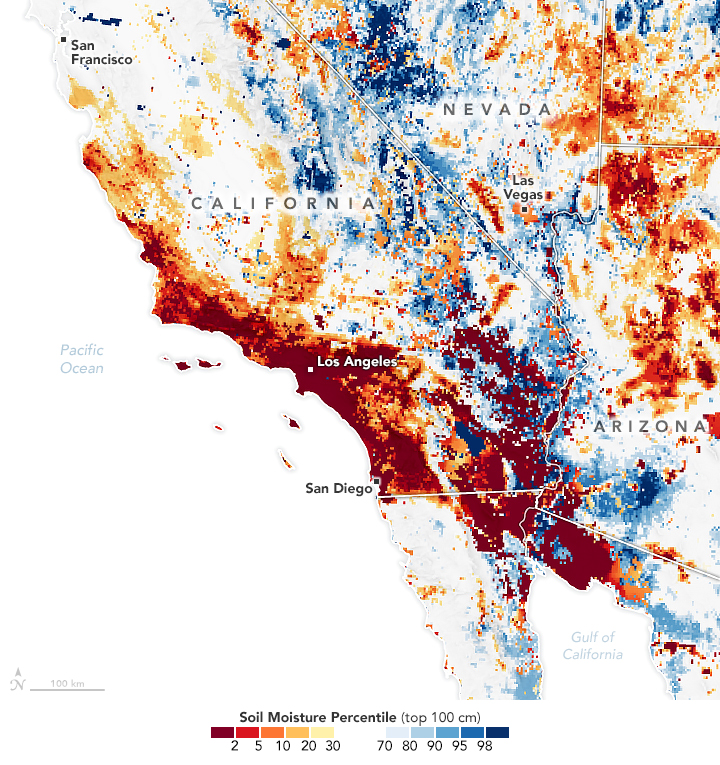
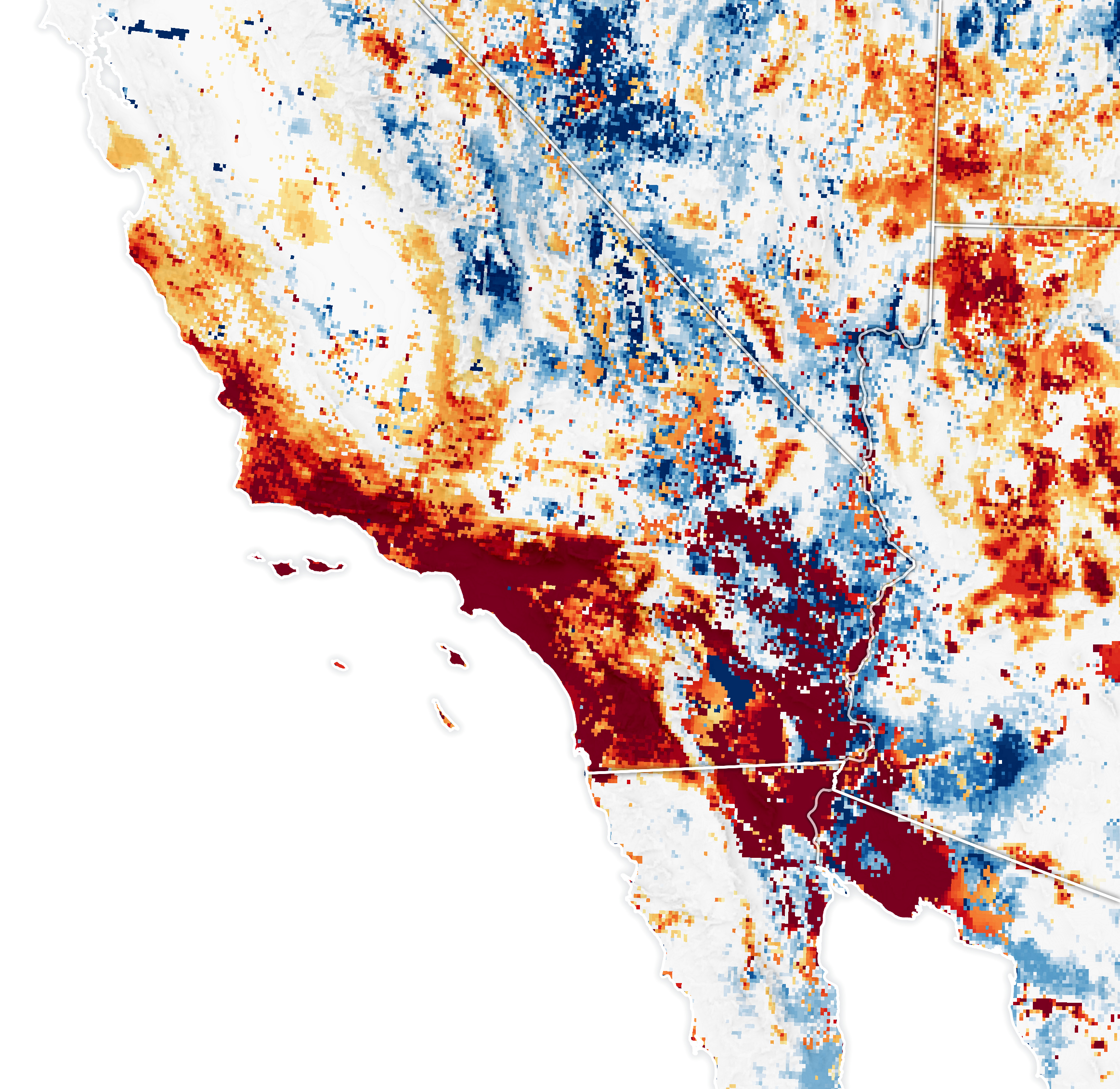
Fuel for California Fires
Published January 30, 2025
The buildup of vegetation and a rapid shift from wet to dry conditions played a role in the destructive blazes.
Related images:
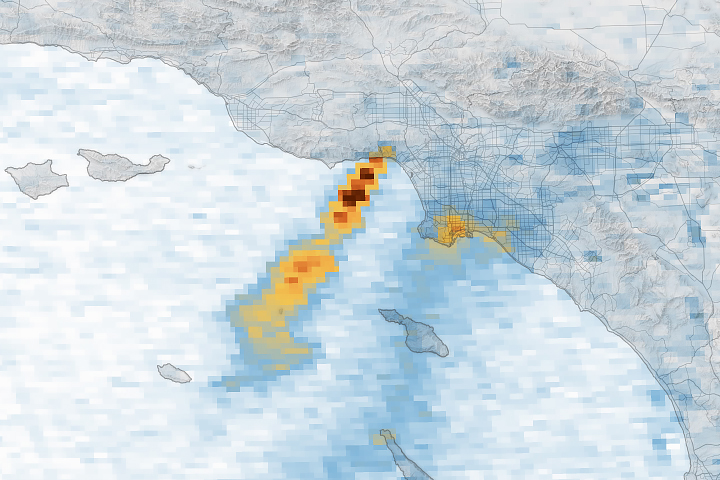
Unhealthy Skies over Los Angeles County
Published January 17, 2025
A series of images captured by NASA’s TEMPO sensor show the shifting location of nitrogen dioxide as destructive fires raged and smoke plumes streamed over the region.
Related images:
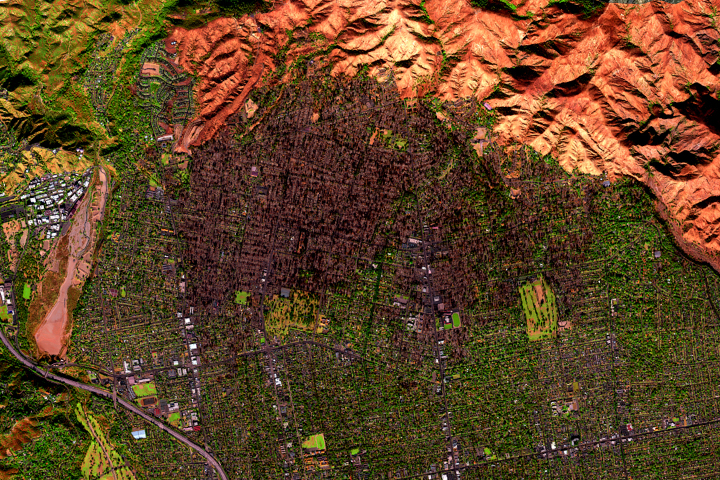
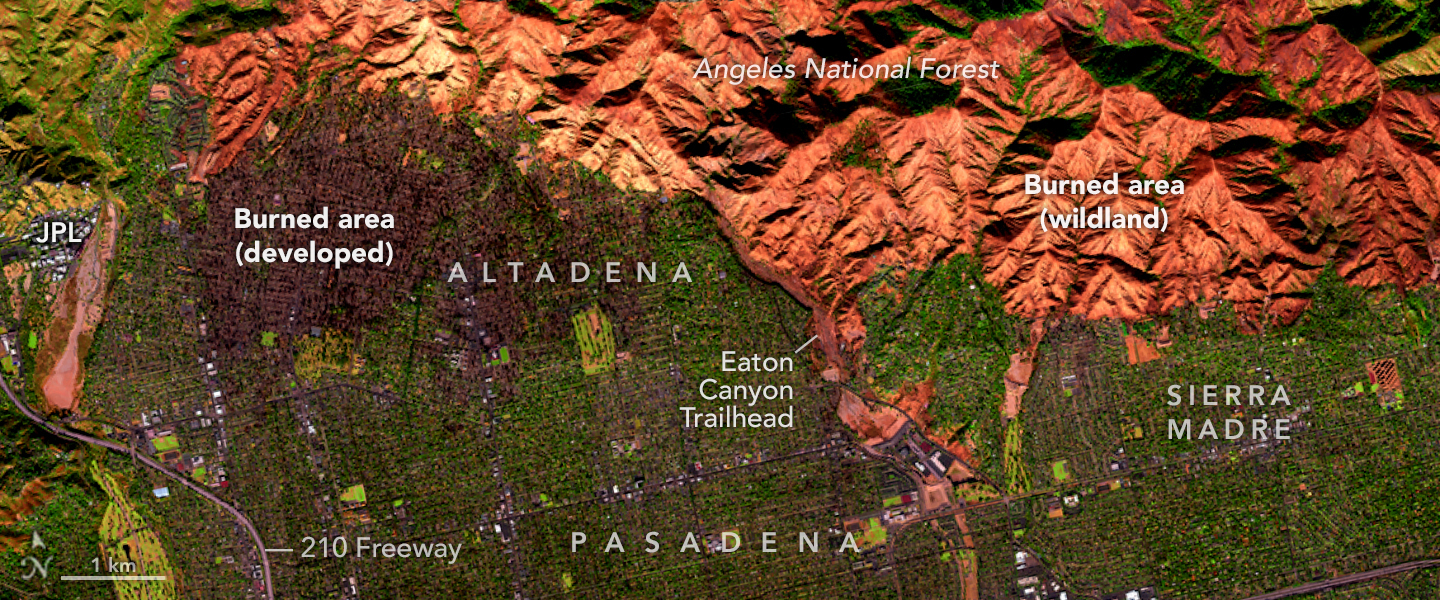
Eaton Fire Leaves California Landscape Charred
Published January 15, 2025
A NASA airborne instrument captured images of the fire’s aftermath in and around Altadena.
Related images:
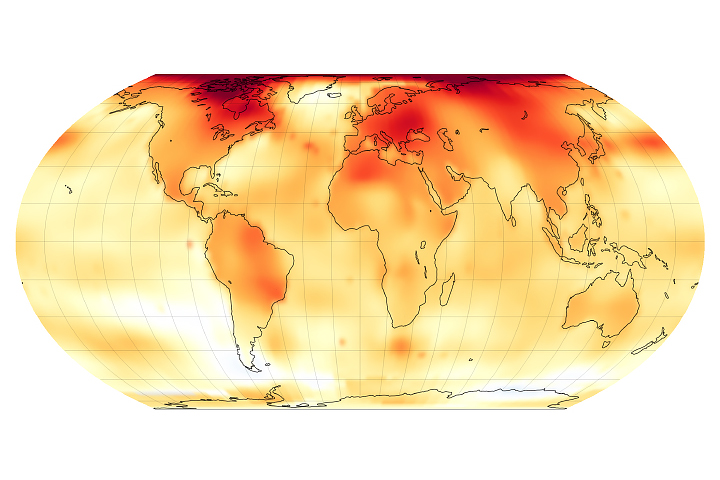
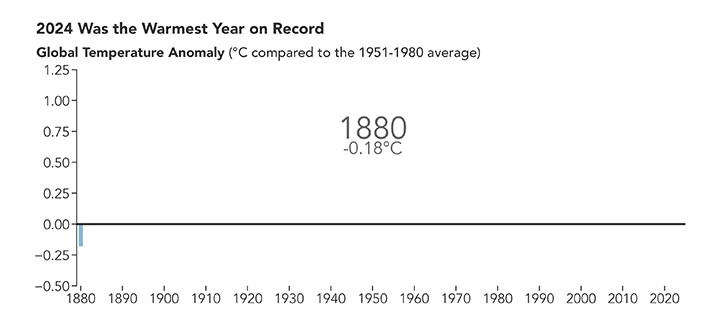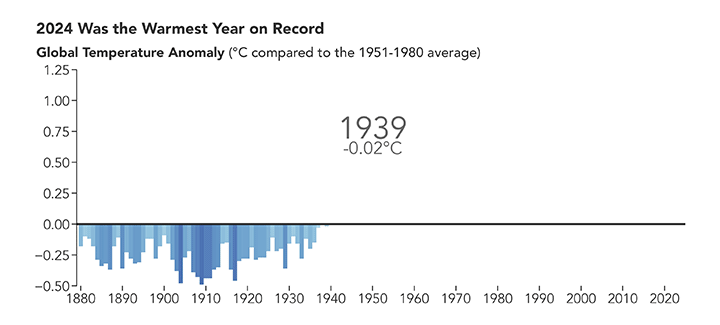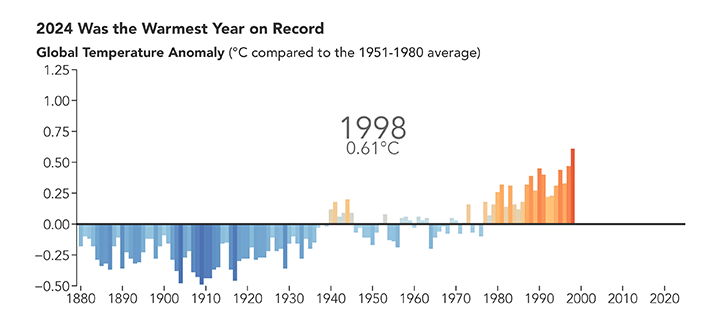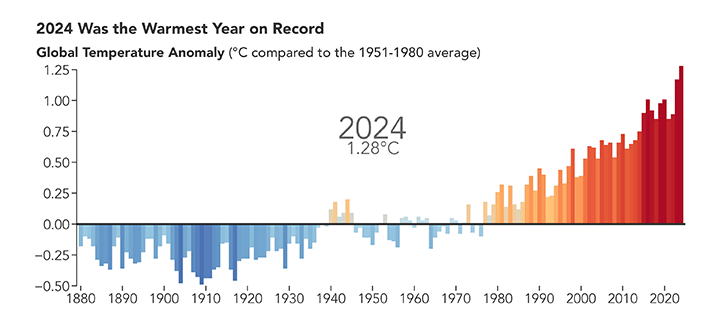
2024 Was the Warmest Year on Record
Published January 10, 2025
A NASA analysis shows that global temperatures in 2024 were 1.28 degrees Celsius (2.30 degrees Fahrenheit) above the agency’s 20th-century baseline.
Related images: